Elliott Wave Theory
Introduction to Elliott Wave Theory
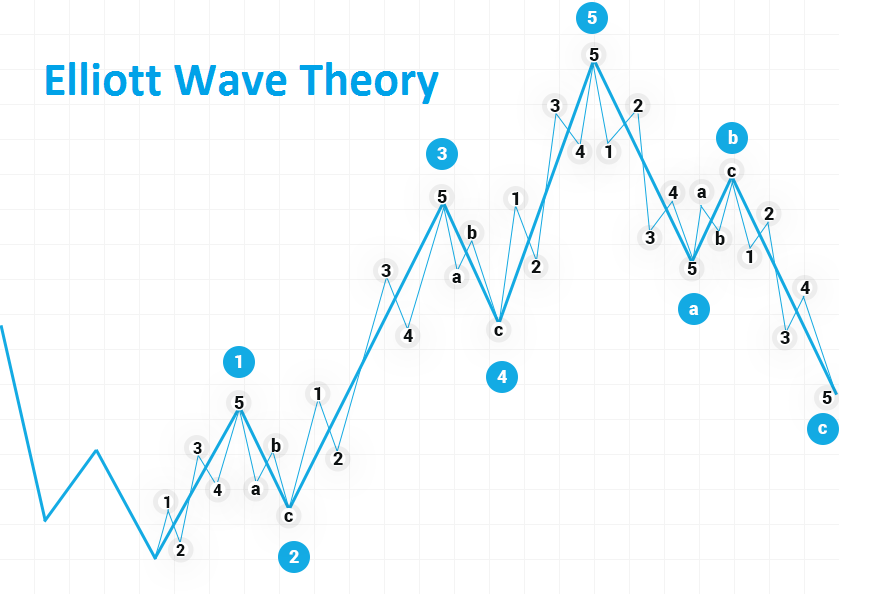
Ralph Nelson Elliott developed Elliott Wave Theory in the 1930s.1 Elliott believed that stock markets, which are generally considered more random and chaotic, were in fact traded in repeating patterns. In this article, we take a look at the history of Elliott's wave theory and its application to trading.
WAVES
Elliott has suggested that financial price trends system on the psychology of the dominant investor. He found that fluctuations in mass psychology always manifested in the same recurring or "vague" fractal patterns in financial markets. Elliott's theory is similar to Dow's theory in that they both recognize that stock prices move in waves. But because Elliott also recognized the "fractal" nature of markets, he was able to break them down and analyze them in much more detail. Fractals are mathematical structures that repeat themselves over and over on a smaller and smaller scale. Elliott found that stock index pricing models were structured in the same way. He then began to examine how these repeating patterns could be used as predictors of future market movements.
1st impulse:
Momentum is the most common motivational wave and it is also the easiest to recognize in a market.
Like all motion waves, the pulse wave has five sub-waves: three motion waves and two corrective waves called the 5-3-5-3-5 structure.
However, the creation of the wave is based on a set of rules.
If any of these rules are violated, the pulse wave will not form and we will have to rename the suspect pulse wave.
The three rules of pulse wave formation are as follows:
Wave 2 cannot go back more than 100% of wave 1.
Wave 3 can never be the shortest of waves 1, 3, and 5.
Wave 4 can never overlap with Wave 1.
2nd diagonal:
Another type of driving wave is the diagonal wave, which like all driving waves is made up of five sub-waves and moves in the direction of the trend. The diagonal looks like a wedge that can expand or contract. Also, the partial waves of the diagonal may not count to five, depending on the type of diagonal observed. Like other moving waves, each partial wave of the diagonal wave does not completely traverse the previous partial wave. Also, sub-wave 3 on the diagonal is not the shortest wave.
Diagonals can be subdivided into start and end diagonals.
The final diagonal usually occurs on wave 5 of a pulse wave or the last wave of corrective waves, while the main diagonal can be found on wave 1 of a pulse wave or wave A of a zigzag correction.
3. Zigzag:
The zigzag is a corrective wave made up of 3 waves called A, B, and C that moves sharply up or down.
Waves A and C are moving waves, while wave B is corrective (often with 3 sub-waves).
Zigzag patterns are sharp declines in a bullish rally or advances in a bearish rally that essentially correct the price levels of previous momentum patterns.
Zigzags can also be formed in a combination known as double or triple zigzags, with two or three zigzags connected by another correction axis between them.
Triangle:
The triangle is a pattern made up of five sub-waves in the form of a 3-3-3-3-3 structure called A-B-C-D-E.
This corrective diagram shows a balance of forces and extends laterally.
The triangle can expand, each of the following partial waves is enlarged or contracted, that is, wedge-shaped.
Triangles can also be classified as symmetric, descending, or ascending, depending on whether they point to the side, up with a flat top, or down with a flat bottom.
Partial waves can be formed in complex combinations. In theory, it may seem easy to spot a triangle, but it may take a little practice to identify it in the market.
Elliott Wave Trading Benefits
As a diagnostic tool for identifying potential business opportunities, Elliott Wave Theory offers value by providing a structure for organizing price action information into easy-to-understand graphical representations. With a broad understanding of the rules of this theory, even beginners can begin to use the theory to support their strategies.
At the same time, the popularity of Elliott Wave Trading is an advantage in itself: since it is rooted in consumer psychology, its relevance to forex trading is greatest when a large group of traders observe these patterns and act on them. they. information.
Disadvantages of Elliott Wave Trading
Despite its advantages, Elliott's wave theory also has limitations that can create complications and lead to inaccurate conclusions during business analysis. While Fibonacci models and similar tools provide clear indices and thresholds for traders to observe, Elliott Wave Theory is more subjective when it comes to identifying patterns. Traders must identify these patterns for themselves, and the price movements that mark the start and end of a wave can vary in interpretation from one trader to another. For this reason, some critics argue that this theory is too arbitrary to provide consistent advice for trading read more.


Comments
Post a Comment